Recently, the research team led by Professor Shimou Chen and Associate Professor Ying Xiao from the CMSE published a review article titled Progress and Challenges of Transition Metal-Based Catalysts Regulation for Li-CO₂ Batteries in Energy Storage Materials. This work analyzes the structural characteristics required for ideal catalysts in Li-CO₂ battery applications, comprehensively discusses cutting-edge modification strategies and underlying mechanisms of various transition metal (TM)-based catalysts, and proposes insights into future research directions and key challenges to be addressed.
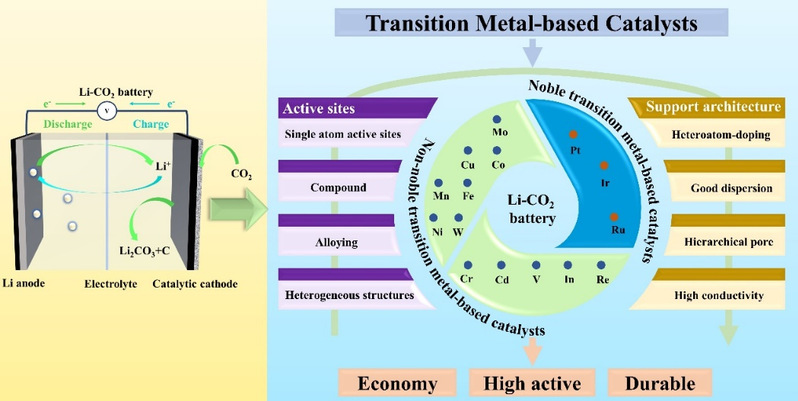
Application and hot regulation strategies of TM-based catalysts in Li-CO₂ batteries.
Li-CO₂ batteries involve complex gas-liquid-solid triple-phase reactions, making the microscopic structural design and activity regulation of catalysts crucial for achieving superior battery performance. Against this backdrop, this review comprehensively summarizes the application of TM-based catalysts in Li-CO₂ batteries, detailing design strategies, synthesis methods, key challenges, and specific mechanisms for various transition metal catalysts—including Ru, Ir, Pt, Mo, W, Co, Cu, Mn, Fe, Ni, Cr, Cd, V, In, and Re. Furthermore, it addresses current controversial issues and future challenges in Li-CO₂ battery research, aiming to provide effective guidance for designing advanced catalysts for Li-CO₂ batteries.
The first author is Shasha Xiao (2023 Master's candidate), with co-corresponding authors Prof. Shimou Chen and Assoc. Prof. Ying Xiao from Beijing University of Chemical Technology. Beijing University of Chemical Technology is the primary affiliation. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
The link to the paper is:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405829725000480


